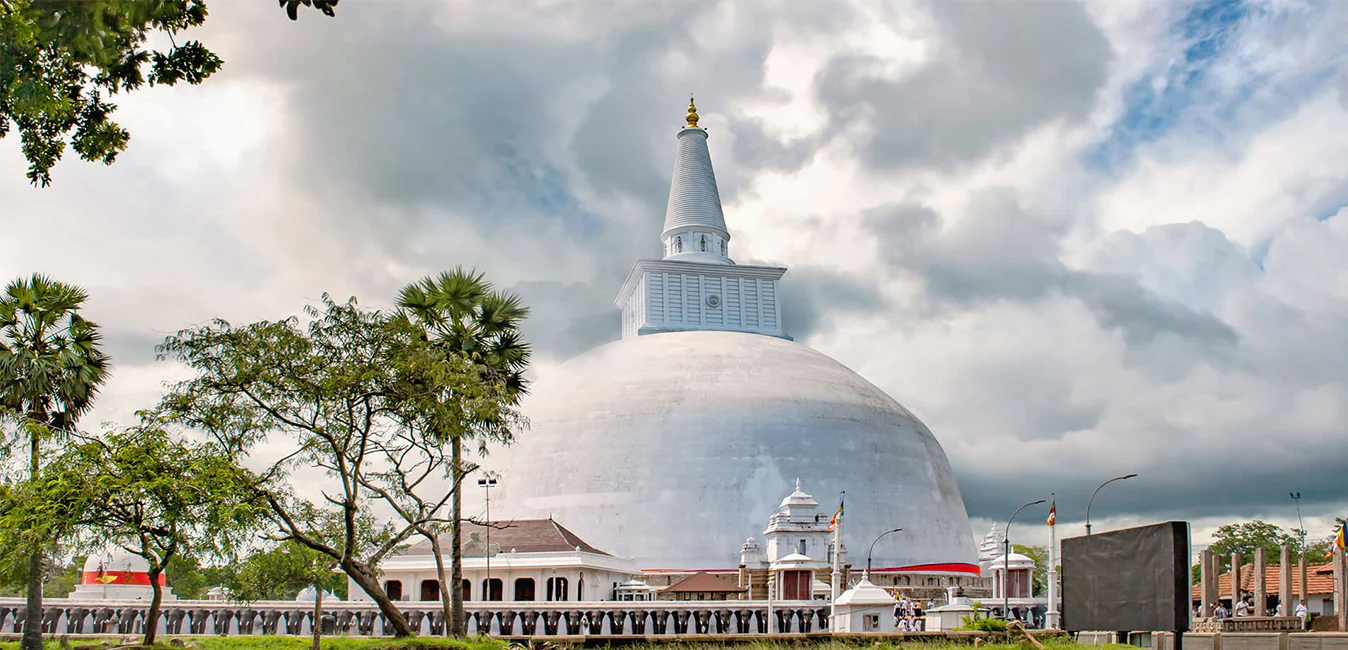
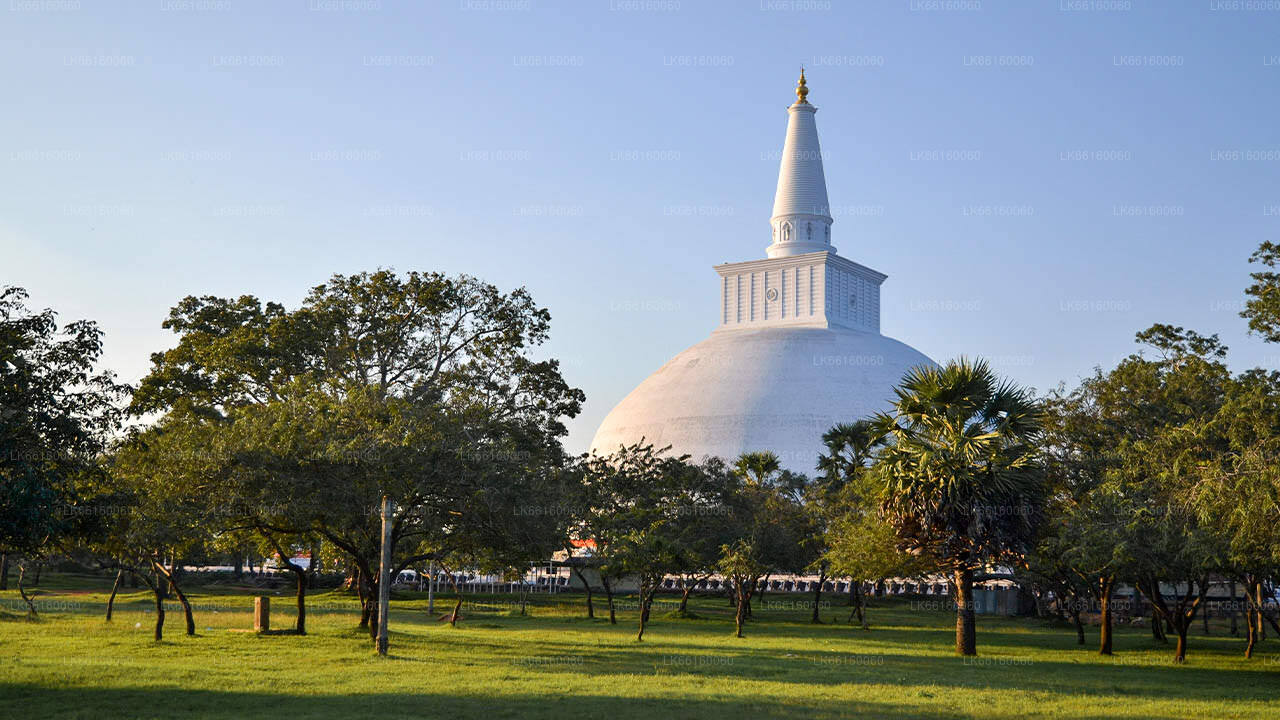
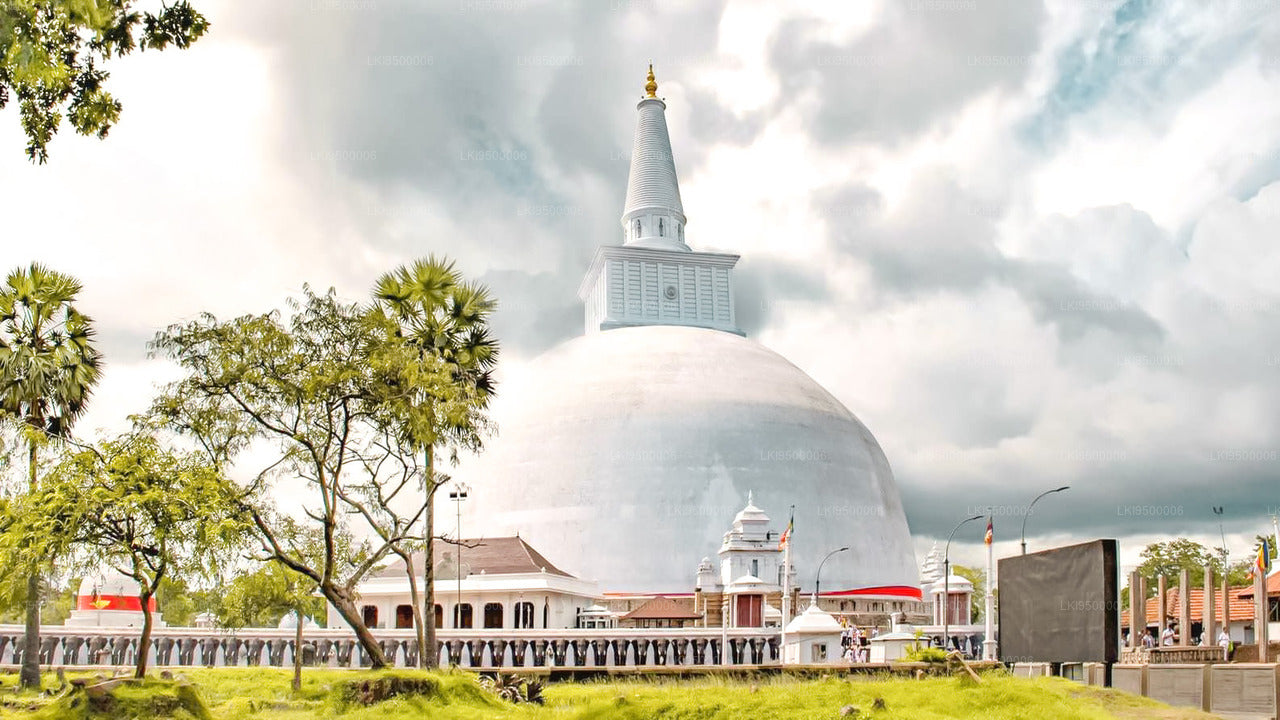
Anuradhapura City
Anuradhapura is belongs to the North Central Province in to Sri Lanka. Anuradhapura is one of the ancient capitals of Sri Lanka, famous for its well-preserved ruins of ancient Lankan civilization. The city, now a UNESCO World Heritage Site, lies 205 km north of the current capital Colombo in Sri Lanka.
Medirigiriya Vatadage
Medirigiriya Watadageya in Sri Lanka is a monastery located in the kingdom of Polonaruwa, dating back to over two millennium. The centerpiece or point of interest of the whole monastery is the Medirigiriya Vatadage. It was an architectural masterpiece of those early eras which housed the Stupa completely within it. Only 7 such stupa houses remain today in Sri Lanka.
The earliest references to this monastery were recorded in the 2nd century AD, though many clues point towards an even longer history.
The History
Records during the time of King Kanitta Tissa (AD 192 – 194) of Anuradhapura show that this Vatadage was much worshipped and respected at that time. However the ancient brahmi characters engraved in the bricks and the stone carvings, which pre date carvings found in the other Vatadages, point towards a long history dating from the pre-Christian Era. The monastery was supported by, and was donated to by many kings throughout Sri Lanka’s history. In particular, the stupa which forms the centerpiece of the Vatadage appears to have been built in the time of Aggabodhi I (564 – 598 AD).
The Medirigiriya Watadageya in Sri Lanka was a building supported by three concentric rings of pillars, and housed the stupa completely. The pillars and ruins still stand today.
The Structure
The Medirigiriya Watadageya in Sri Lanka was built on a rocky outcrop. It had a single entrance facing north. The doorway was a huge carved stone frame built at the bottom of a staircase. The frame measured 9.75 feet in height and 4.75 feet in breadth. The doorway was followed by a climb of 27 stone steps to a large resting area. Four steps lead from the resting area to the actual Stupa house. The Stupa House had a low stone wall, about a meter tall, which ran around it. Seated against the wall facing the four cardinal directions were four exquisite stone Buddha statues. There was a huge 33 feet-long sleeping Buddha in the Stupa House. The Stupa reigned in the center.
The stupa was surrounded by stone pillars in three concentric rings. The outer ring had 32 pillars standing at nine feet, the middle ring 20 pillars standing at 16 feet, and finally, the inner ring had 16 pillars standing at 17 feet. Some archaeologists argue that there never was a roof, while other’s say that the remaining pillars in the ruins still standing prove that they supported a roof. The heights of the rings of pillars point toward a roof that would have been very tall in the center to accommodate the spire of the Stupa, while sloping downward in a dome-like fashion to a comparatively lower point at the outer edges.
The ruined but still elegant Medirigiriya Vatadage is a prime example of the advanced stone crafting practiced by the craftsmen of Ceylon throughout the ages.
Other Features
The other features that the Monastery of Medirigiriya once had were the two bathing ponds, a cave with signs of use by the ancient monks, a toilet, a hospital that was quite advanced for its time and a medicine boat made of hard rock shaped to fit any type of body structure. There are also three stone inscriptions still to be seen. Two of them are about the management of the hospital and the provision of food. The third is inscribed in ancient Tamil lettering.
The Medirigiriya Vatadage was rediscovered in the late 1800s.
Abandonment and Present State
Medirigiriya was abandoned after the invasion of Kalinga Magha. Over half a millennium later in 1897, Mr H.C.P Bell rediscovered it during a trek in the jungle and immediately realised its importance. He called it an architectural jewel and had restoration work done on it. The restoration was completed in 1945 and declared open to the public.
About Anuradhapura District
Anuradhapura is belongs to the North Central Province in to Sri Lanka. Anuradhapura is one of the ancient capitals of Sri Lanka, famous for its well-preserved ruins of ancient Lankan civilization. The city, now a UNESCO World Heritage Site, lies 205 km north of the current capital Colombo in Sri Lanka.
In the sacred city of Anuradhapura and in the vicinity are a large number of ruins. The ruins consist of three classes of buildings, dagobas, monastic buildings, and pokuna (ponds). The city had some of the most complex irrigation systems of the ancient world, situated in the dry zone of the country the administration built many tanks to irrigate the land. Most of the civilians are Sinhala, while Tamils and Sri Lankan Moors live in the district.
About North Central Province
North Central Province which is the largest province in the country covered 16% of total country's land area. North Central Province consist two districts called Polonnaruwa and Anuradhapure. Anuradhapura is the largest district in Sri Lanka. Its area is 7,128 km².
North Central Province has numerous potentials for Investors to start their Businesses, especially Agriculture, agro based industries and Livestock sectors. More than 65% of North Central Province's people depend on basic Agriculture and agro base industries. NCP also called "Wew Bendi Rajje" because there are more than 3,000 medium and large scale tanks situated in the province. Sri maha bodiya, Ruwanweli seya, Thuparama dageba, Abayagiri Monastry, Polonnaruwa Rankot wehera, Lankathilake are scared